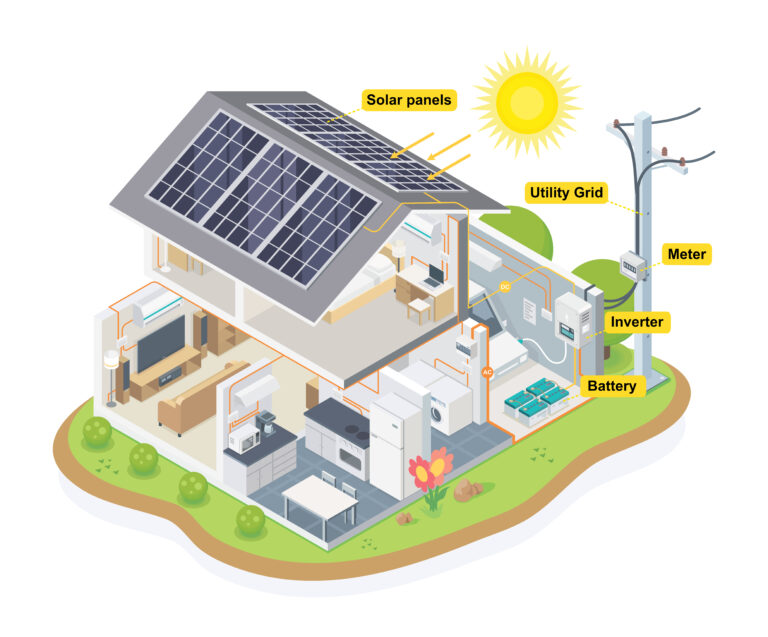
Solar panels have become a familiar sight in our communities, adorning the roofs of buildings and according to MCS certified, 1.3 million homes in the UK. Despite their prevalence, many still ponder the mechanics behind their functionality. In essence, solar panels harness sunlight and transform it into electricity through specialized structures known as ‘photovoltaic cells’ within the panels. These cells ingeniously generate an electrical current that can be utilised within our households.
This solar technology not only provides a renewable energy source but also a clean one, offering an alternative to traditional fossil-fuelled power. By reducing carbon emissions and curbing the escalating costs of energy, solar panels are becoming a must-have asset for both the environment and homeowners. In this article, we will delve deeper into the inner mechanics of solar panels, explore their components, and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy for our planet.
How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, convert solar energy into usable electricity. The number of solar panels installed on a rooftop determines the amount of electricity generated. Here is a step-by-step guide on how solar panels work:
Solar panels consist of metal sheets inside a glass casing that contain a series of cells known as photovoltaics (PV). PV cells are made of a thin, semi-conductive material with two silicon layers. One layer is positively charged, and the other is negatively charged, creating an electric field. When sunlight hits the PV solar cell, it causes motion within the electric field, generating an electrical current.
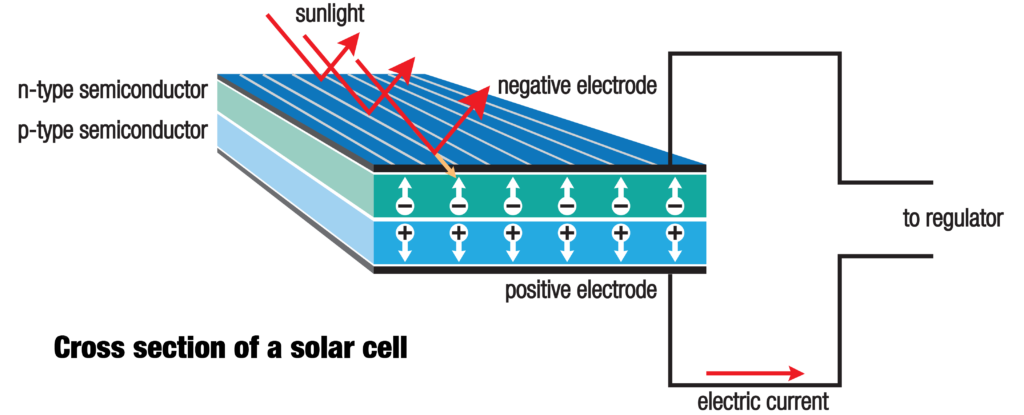
Once the electric current is generated, it can be redirected from the solar panels. At this point, the electricity produced is in a form known as a direct current (DC), and for us to use this on our electrical devices at home, it needs to be converted to an alternating current (AC).
To convert DC electricity to AC, a solar inverter is used. An inverter is an important part of a solar power system, in british temperatures it is best to install them inside the house, but there are inveters desgined to be outdoors if needed. In home systems, there are Three types of inverters: a ‘string inverter’ (a central inverter), a hybrid inverter or micro-inverters. Micro-inverters are used only on individual solar PV panels and are not likely to be seen in larger systems. A string inverter will be used for most home setups requiring multiple solar panels. This is so-called because each solar panel is wired into a central inverter (much like a series of strings coming together). A hybrid inverter does the same job as a string, but allows a battery to be coupled up and charged by the solar system. In 2024, hybrid inverters are the most popular choice amongst the british public due to the increased financial benefits of having solar storage batteries.
In some modern models, the inverter can also be used as a point to monitor your power generation and usage levels. Depending on the model, you can access these details online or through an app.
From here, you now have a usable source of electricity that can power your home. Three things can happen next – you can use the produced electricity or store any that you don’t use in a solar battery. If at any time you are generating more than what you are using, you can automatically sell back electricity to the grid using the smart export guarantee (SEG)
It’s important to note that solar panels are most effective in direct sunlight, but they do still work on cloudy days. Although the efficiency of solar panels decreases in cloudy conditions, they can still produce about 10-25% of their rated capacity, depending on the thickness and density of the cloud cover source.
Since 2020, homeowners in England, Scotland, and Wales have been able to receive payments for each renewable energy unit they produce and export to the grid under the Smart Export Guarantee source.
In conclusion, solar panels work by converting solar energy into usable electricity through a series of PV cells, inverters, and batteries. They are an effective and sustainable way to generate free electricity and reduce your carbon footprint.
The Different Types of Solar Panel
Monocrystalline or Polycrystalline?
When choosing solar panels, you will come across different types of solar panel materials. The two main types are monocrystalline & polycrystalline, with thin film panels not used much anymore. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on your needs, budget, and space.
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline | High efficiency up to 30%, long lifespan, takes up less space | More expensive |
| Polycrystalline | Lower cost than monocrystalline, average efficiency up to 22% | Lower efficiency than monocrystalline, takes up more space |
| Thin-Film | Least expensive, flexible and lightweight, works well in low light conditions | Lower efficiency, shorter lifespan |
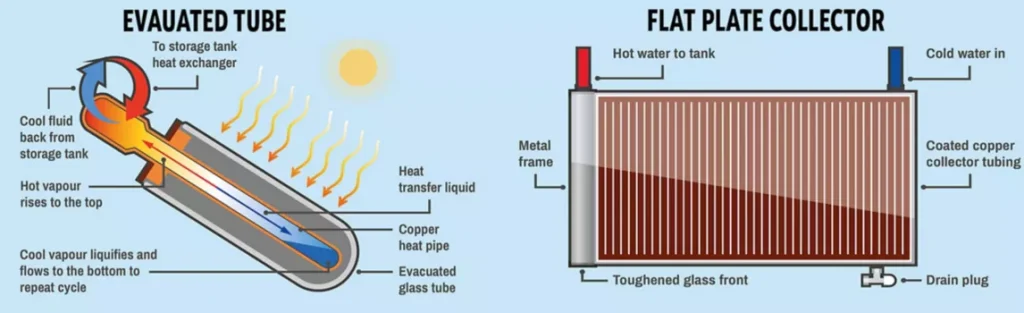
What Are Solar Thermal Panels?
The most popular solar panels are photovoltaic, which are electricity producing panels, however solar thermal panels use sunlight to generate heat which can be used for your central heating system and hot water needs. Although both are utilising solar energy, solar thermal panels do have a use for some homes and businesses, but the disadvantage is that solar thermal power cannot be coverted in to electrical power, unlike solar PV. Electrical power can be used for your basic electrci needs, but also used for heating too when conbined with an immersion water heater, or an air sourced heat pump.
How Long Do Solar Panels Last?
The lifespan of solar panels depends on the type of panel and how well they are maintained. Monocrystalline panels have the longest lifespan, usually 25 years or more. Polycrystalline panels have a lifespan of 20-25 years, while thin-film panels have a lifespan of 10-15 years. Proper maintenance can extend the lifespan of your solar panels. This includes cleaning every year or two, checking for damage, and ensuring that the panels are operating at maximum efficiency, which you can do through a mobile app on most new systems.
In conclusion, when choosing solar panels, you need to consider the type of panel material, whether you need solar PV or solar thermal panels, and the lifespan of the panels. By understanding these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the solar panels that are right for your needs.
How to Choose the Best Solar Panel System for Your Home?
Choosing the best solar panel system for your home is not the easiest thing to decide on. However, our website www.comparerenewables.com makes it easy for you to find MCS accredited solar installers. Simply fill in your details and receive quotes from trusted installers. When choosing a solar panel system, consider the following factors:
- Your budget
- Your roof space
- Your energy & battery
- The efficiency of the panels
- The warranty offered by the manufacturers
An expert will come out to see you and provide a detailed quote. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and compare quotes before making a decision.
Take a look at our guide on the costs involved to install a solar system in your home.
Related Posts:
How Does a Solar Battery Work?
Storing Energy
Solar batteries store energy generated by solar panels that is not immediately used. This stored energy can be used during periods of low solar generation, such as at night or on cloudy days. The process of storing the energy involves converting the stored direct current (DC) electricity produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used in your home. This is done through the use of a hybrid solar inverter, which also manages the charging and discharging of the battery.
Are Solar Batteries Worth It?
The cost of solar batteries has decreased in recent years, making them a more affordable option for homeowners. However, the cost-benefit analysis of installing a solar battery depends on a variety of factors, including your energy usage, the size of your solar panel system, and your location. In areas with high electricity rates or frequent power outages, solar batteries can provide significant savings from your electric bill as well as peace of mind. Additionally, solar batteries allow you to operate your home on a fully renewable energy source, reducing your carbon footprint.
Using my experience I have found that solar batteries can be a valuable addition to a solar panel system, providing backup power and reducing energy costs. The best way to calculate the right battery size for your home is to look at you annual usage, divide by 365, to get your daily usage, then get a battery that is between 30% to 50% of you annual consumption, that should be enough to cover you at night and on days of low light. However, it is important to carefully consider your individual circumstances and remember, capturing all of your solar electrcity is not the aim here, you want enough batteries for the average day, not your highest day of consuption, because you will not get a good return on investment on that extra battery which be used on a few days per year.

Advantages of Having Solar Panels at Home
Installing solar panels at your home comes with a wide range of benefits. Here are some of the advantages that you can enjoy:
Saving Money: By installing solar panels on your roof, you can produce your electricity supply, which means you no longer need to rely on a grid supplier for the majority of your consumption. This can significantly cut down your electricity bills. The only electricity expenditure you need to consider is if you use the grid during the night and the standing charge.
Reducing Your Carbon Footprint: Solar panels are one of the best steps you can take if you’re looking for a way to go green and cut down harmful emissions. Most electricity suppliers use fossil fuels such as oil, gas or coal to produce power, which creates harmful carbon dioxide. On the other hand, solar power is a clean, non-polluting, renewable energy source that is also free!
Becoming Independent from the Grid: The National Grid provides most people with electricity, fuel prices are prone to sharp, unstable price changes. By switching to your supply, you can become less dependent on the grid and know that you have a consistant power supply from solar panels.
Low Maintenance: Solar panels have a long lifespan of at least 25-30 years and come with average warranties of around 20+ years, meaning you don’t have to worry about expensive replacements or constant upgrades.
Earning Money: Through various incentives and schemes, homeowners with solar panels may be able to receive payments for any excess electricity through more recent export tariffs. This helps significantly in recouping the cost of the installation, making it an even more lucrative long-term investment.
Do Solar Panels Work in Bad Weather?
It is a common misconception that solar panels only work on hot and sunny days. However, solar panels can still generate power in almost any type of weather, including cloudy days, rain, and even snow. The only difference is that they won’t produce as much as they would on a brighter day.
On severely overcast and cloudy days, your solar panels’ power output will be impacted if the cloud cover lasts most of the day. One way to determine if your solar panels are getting any sun is to check for shadows outside. If shadows are being produced, your panels will likely get some sunlight. No shadows would suggest the clouds are too thick for any sun to get through.
It is important to understand your unique solar panel setup, especially before you purchase, such as your location, the type of panels, and how you will source electricity should your supply drop in cloudy weather and in the evening. The best way to improve solar panel performance in bad weather is to use a battery storage back up system, which will store excess energy for use during periods of low production or bad weather.
How much do solar panels cost?
The cost of solar panels depends on various factors such as the size of your home and the number of panels you need. Typically, solar panel systems cost between £5,000 – £15,000. The size of the system is measured in kilowatts (kWp), and the cost of a 4kWp system, which is the average size for a UK home, is around £8,000. If you add a hybrid inverter on and a battery storage, you can expect to pay an extra £3,000 and upwards, depending on the amount of battery storage which you require.
We have a guide to find out which system will be best for your home – How Many Solar Panels Do I Need?
By generating your own electricity, you can reduce your dependence on the grid and save money on your electricity bills. We recommend speaking to professionals to get the best idea of how much solar panels cost. By getting multiple quotes from qualified installers, you can get trustworthy advice and find the best prices simultaneously!

How to Choose a Solar Panel Installer
Choosing the right solar panel installer is crucial to ensuring that your solar panel system is installed correctly and efficiently. Here are some tips on how to choose the best solar panel installer for your needs:
Look for an installer who is MCS accredited. This means that they have been vetted and approved by the industry standard body for renewable energy installers in the UK.
Get quotes from at least three different installers. This will allow you to compare prices and services and choose the one that best fits your needs.
Check customer reviews and references. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous customers to get an idea of the quality of service that the installer provides.
Make sure the installer offers a warranty on their work. This will give you peace of mind knowing that if anything goes wrong with your system, the installer will be there to fix it.
Consider financing options. Many installers offer financing options to help you spread the cost of your solar panel system over time. You will also get cover using the FCA section 75 rule.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you choose the best solar panel installer for your needs and get the most out of your solar panel system.
Related Post:
4 Ways To Make Money With Solar Panels
Using Electricity From Your Solar Panels
Instead of relying solely on electricity from the grid, your solar panels produce their own power, reducing the amount of electricity you need to purchase from the utility company and saves you money for every kWh.
Store Energy in Your Battery to Use at Night
Solar panels work only work during daylight hours, meaning they become useless when it’s dark. This doesn’t just mean nightfall; in low light days through the winter, they won’t produce as much electricity as in good conditions. Installing a solar storage battery to store the excess energy generated during the day for use at night. This prevents you from having to buy electrcitiy from the grid at night time and is a great way to maximise the return on your investment.
SEG Payments
The Smart Export Guarantee (SEG) is a government scheme that pays you for the excess electricity you generate and export to the grid. This means that you can earn money from your solar panels even when you’re not using the energy yourself. The SEG payments are made by energy suppliers and are based on the amount of energy you export. The rate you receive will depend on your supplier, so it’s worth shopping around to find the best deal.
Overnight Charge Your Battery on the Cheap Rates
If you have a solar storage battery, you can charge it overnight during off-peak hours when electricity rates are cheaper. This means that you can use the stored energy during peak hours when rates are higher, maximising your savings and return on investment.
In conclusion, by using a combination of SEG payments and solar storage batteries, you can maximise your return on investment with an optimal setup. However, it’s important to choose a trusted installer and consider all factors before investing in solar panels.
Solar Panel Rules & Regulation
The Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) is the governing body when It comes to installation standards and good practice. All installers who claim to have a level of competency should be registered with the MCS to evidence their quality. The only other main area of external influence is with your local Distribution Network Operator, who will have an input on what system you are able to have at your home.
G98 or G99 Application
When installing solar panels in the UK, a notification must be made to the energy grid. This notification is called a G98 or G99 application, depending on the size of the system. Installers will usually handle this process for you, but it’s important to understand what each application entails.
G98
A G98 application is required for solar panel systems with an inverter size of less than 3.68kW. This application process is relatively straightforward and involves notifying your local District Network Operator (DNO) within 28 days of commissioning the system. Once the DNO receives the notification, they will review the application and confirm that the system meets safety and technical standards.
G99
If your solar panel system has an inverter size of more than 3.68kW, you will need to submit a G99 application. This process is more complex than a G98 application and requires a more detailed review by your DNO. The purpose of the G99 application is to ensure that your solar panel system is safe and won’t cause any disruptions to the energy grid.
The G99 application process involves submitting detailed technical information about your system, such as its maximum export capacity and fault ride-through capability. The DNO will review this information and may require additional testing or modifications to ensure that your system meets all safety and technical standards.
Once your G99 application is approved, you will receive a connection agreement from your DNO. This agreement outlines the terms and conditions for connecting your solar panel system to the energy grid and may include requirements for ongoing maintenance and monitoring.
It’s important to note that the G99 application process can take several weeks or even months to complete, so it’s important to plan accordingly and work closely with your installer to ensure that all requirements are met.